How GPT-4.5 & GPT-5 Are Changing Work Across Industries
Generative AI is transforming work across industries. With GPT-4.5 already released (as a research preview in early 2025) and GPT-5 on the horizon, companies are integrating AI into everyday tools and workflows. In fact, a recent Google Cloud report catalogued 601 real-world AI use cases from leading organizations, showing how AI is “here, AI is everywhere” in enterprises. Innovations like Microsoft’s Copilot and Google’s Gemini are automating tasks from email drafting to data analysis. As one analyst notes, about 80% of jobs could incorporate generative AI capabilities. In this blog, we explore how next-generation models (GPT-4.5 and GPT-5) are enabling new productivity apps and use cases in marketing, HR, legal, customer service, and software development. We’ll also highlight how digital agencies (like Nuform Social) leverage AI for SEO, content personalization, CRM optimization, and marketing automation – with big cost savings and ROI.

The Evolution of Generative AI
Large language models have advanced rapidly. OpenAI’s GPT-4 (2023) brought more knowledge and context to AI chatbots, and GPT-4.5 (early 2025) further scales up training to improve creativity and reliability. In OpenAI’s own words, GPT-4.5 is their “largest and best model for chat yet,” trained with more data and compute. It recognizes patterns better, draws connections, and generates creative insights without explicit reasoning. Early tests show GPT-4.5 feels more natural in conversation, with a broader knowledge base and a higher ability to follow user intent. In practice, GPT-4.5 can more effectively improve writing, aid programming, and solve practical problems – and it even “hallucinates” (makes factual errors) less often.
The next leap, GPT-5, is shaping up to be even more capable. OpenAI CEO Sam Altman hints GPT-5 will be a unified model with built-in chain-of-thought reasoning, combining the strengths of earlier models. It will integrate new modalities (voice, image/video, search) and tools. For example, Altman noted GPT-5 will incorporate “voice, Canvas, search, deep research, and more,” allowing a system to know when to run a quick task versus a long reasoning chain. Although GPT-5’s exact release date isn’t public, industry rumors suggest it could arrive by mid-2025. When it does, GPT-5 is expected to offer even richer, multimodal collaboration – for instance, GPT-4o (the GPT model behind ChatGPT’s image tools) already demonstrates how AI can “transfer between modalities” (text, pixels, sound) in one model.
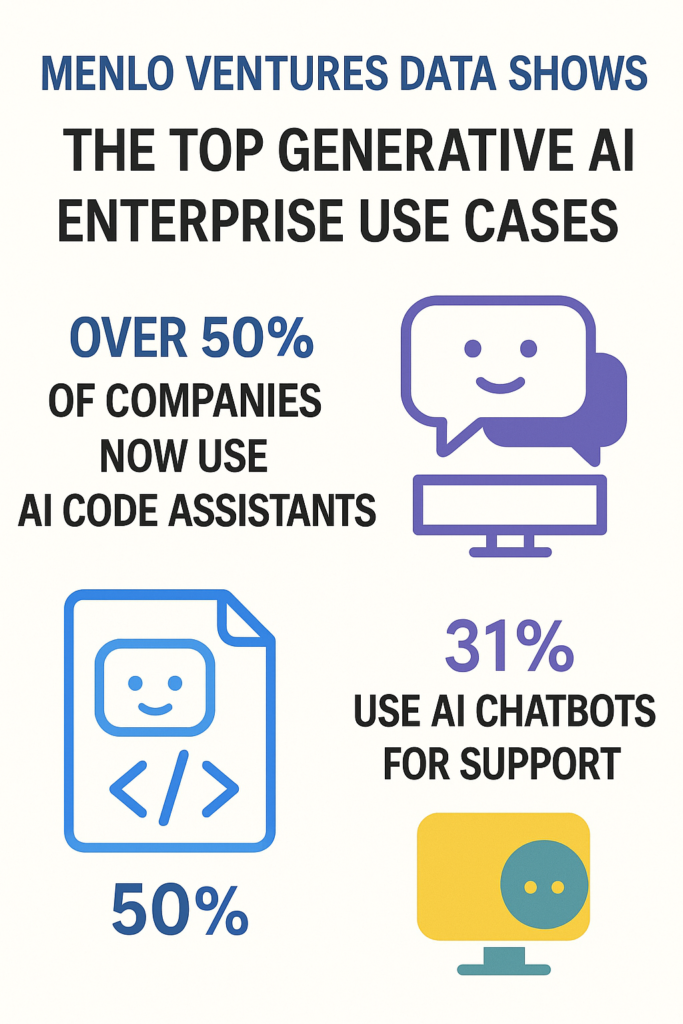
These advances mean future AI assistants will handle more complex tasks and integrate into software. As one industry survey shows, organizations are already prioritizing practical, ROI-driven AI applications: code assistants top the list (51% of enterprises use them), followed by customer service chatbots (31%), semantic search tools, data transformation, and meeting summaries. In short, the technology has caught on quickly – GPT-style models are no longer laboratory curiosities but embedded in business processes. The figure below (from Menlo Ventures) highlights that code generation and chatbots lead in usage.
Integration into Productivity Tools and Business Operations
Generative AI is already baked into many productivity suites and platforms. Office suites and collaboration tools now include AI copilots. For instance, Microsoft 365 Copilot (in Word, Excel, Teams, etc.) automatically drafts documents, analyzes data, and summarizes communications. Google’s Gemini tools (in Workspace) help write emails, design slides, and even draft code. Many companies report dramatic efficiency gains. For example, a mining firm using Copilot cut 2,200 staff-hours per month of mundane work by automating routine writing and analysis. Another company saw a 10-fold productivity boost by deploying an in-house AI chatbot to help employees find information.
Salesforce has embedded generative AI into CRM: its Einstein GPT combines customer data with LLMs to generate tailored content across sales, service, marketing and IT. Salesforce explains that Einstein GPT can write personalized emails for sales reps, craft answers for service agents, create targeted marketing campaigns, and even generate code for developers – all on the fly. Crucially, Einstein GPT operates on a company’s own “trusted, real-time” CRM data, ensuring privacy and compliance. Similarly, Slack added a ChatGPT-powered app that delivers instant conversation summaries and writing assistance.
In software development, AI assistants are mainstream. GitHub Copilot and similar tools (like Codeium, Tabnine, Replit Ghostwriter) automate code writing, test generation, and documentation. A recent survey found 51% of enterprises are using AI code copilots. In practice, developers report big gains: consulting firm Quantiphi saw a 30% increase in developer productivity in a Code Assist pilot. Companies also use AI for testing and project management – for example, Atlassian’s Jira can suggest steps for bug fixes, and GitHub’s code scanning tools are increasingly AI-powered. Overall, by automating repetitive tasks and surfacing insights, generative AI is freeing professionals to focus on higher-value work.
Use Cases by Industry
Marketing and Advertising
In marketing, generative AI enables rapid, data-driven creative work. Marketers can use AI to generate blog posts, ad copy, social media content, and even video storyboards tailored to customer segments. According to Gartner, 75% of marketers say AI will significantly impact their strategy within two years. Tools like OpenAI’s GPT or Jasper let agencies churn out SEO-optimized articles and ads in seconds. They also analyze keywords and competitor content to recommend how to rank higher in search. AI-driven personalization is a game-changer: by analyzing user behavior, AI can customize landing pages and email copy for different audiences. An industry study from Epsilon finds 80% of consumers are more likely to buy when content is personalized.
Real-world results are impressive. One AWS case study reported that a marketing platform built on AI achieved 30× ROI for clients, slashed costs by 90%, and saved 2,000 developer hours (by automating content creation and distribution). In another example, a media agency used Google’s Gemini to launch a personalized ad campaign; it saw an 80% jump in click-through rate, 46% more engaged visitors, and a 97% reduction in cost-per-purchase – all while cutting campaign development time by 50%. These gains free up marketing budgets and let agencies like Nuform Social deliver more campaigns for less money. By automating A/B testing and content variations, they can optimize SEO and outreach at scale.
Content personalization is another focus. AI can segment customers and generate tailored messages. For instance, AI tools can draft hundreds of customized email subject lines or recommend product bundles based on customer profiles. Agencies use this to increase engagement: one founder reports using AI to draft “personalized emails to potential clients in her own voice,” dramatically speeding up outreach. AI also powers interactive content: chatbots on websites can engage visitors with personalized recommendations or quizzes, and gamified experiences (like quiz-style landing pages) can be built with AI logic. These not only boost user engagement but also gather data for CRM systems.
Human Resources (HR) and Recruiting
HR departments are applying generative AI to reduce routine work and improve employee experience. Common use cases include drafting job descriptions, screening candidates, and answering employee queries. For example, HR professionals now often use AI to write the first draft of a job posting or an interview invitation email. In fact, a 2024 survey found 65% of HR teams use AI to generate job descriptions. By automating resume summaries and initial candidate outreach, recruiters save hours and can focus on high-value tasks like interviewing or employer branding strategy.
AI chatbots also serve as first-line HR support. Employees can ask generative-AI–powered assistants about benefits, vacation policies, or training programs. This 24/7 self-service reduces the burden on HR staff. Oracle notes that freeing HR pros from administrative tasks allows them to focus on strategic work (like talent development and workforce analytics). Companies are already reporting benefits: one HR tech survey found that early adopters saw improved hiring, faster onboarding, and higher retention by leveraging AI in HR workflows.
Some large HR service providers are also embedding AI. For example, Randstad – a global talent firm – uses Google’s Gemini across its organization. They report that AI has transformed their work culture, leading to a more diverse and inclusive environment and even a significant drop in sick days. Workforce management company UKG built a generative-AI “conversational agent” for HR administrators. Employees and managers can simply ask this assistant about company policies or get business insights on demand, improving the day-to-day HR experience. Overall, generative AI in HR boosts productivity and employee satisfaction, delivering cost-effectiveness (fewer routine inquiries for HR) and measurable ROI in talent management.
Legal and Compliance
The legal industry is using generative AI to accelerate document work and research. AI tools can draft standard contracts, summarize case law, and review compliance checklists. For example, consulting firm Cognizant built an AI agent (using Google Vertex AI/Gemini) to help legal teams draft contracts, assign risk scores, and suggest ways to mitigate issues. In practice, such systems can reduce review time from days to minutes. A Brazilian firm, Fluna, reports automating the analysis and drafting of legal agreements with AI, achieving 92% accuracy in extracting key data while keeping sensitive information secure. Law firms are taking note: Freshfields is rolling out AI tools firmwide and even developing bespoke AI products for their highly regulated practice areas.
Major legal tech companies have also entered the space. Thomson Reuters (Casetext) offers “CoCounsel,” an AI assistant for lawyers, which can answer research questions, draft clauses, and check documents against legal playbooks. These assistants aren’t replacing lawyers, but augmenting them – allowing paralegals and attorneys to accomplish more with less rote effort. The upshot is clear: document-heavy processes become faster and less error-prone. The cost-effectiveness is significant: by cutting manual review time (and potential human error), generative AI lowers legal spend. Firms using AI report that they can handle larger workloads (or charges) at the same staff levels. Compliance improves too, since AI can be tuned with firm-specific rules. For instance, Fluna’s workflow ensured “security and reliability for sensitive information” as part of its contract automation.
Customer Service
Digital marketing agencies like Nuform Social are at the forefront of applying AI to online strategy. They deploy generative AI in multiple ways:
- SEO & Content Personalization: AI tools can audit websites for keyword gaps and automatically generate SEO-friendly content (blogs, meta descriptions, product pages). They also personalize web and email content based on user data. For example, an agency might use GPT-based tools to produce dozens of content variants for different customer segments, ensuring each user sees headlines and offers tuned to their interests. This level of personalization historically required huge copywriting budgets, but generative AI makes it cost-effective. Studies show AI-driven campaigns dramatically improve engagement: one campaign saw 80% better click-throughs and massive cost reductions.
- CRM Optimization: Integrating AI with CRM systems helps segment customers and craft targeted outreach. Salesforce’s Einstein GPT is a prime example: by combining a company’s own CRM data with LLMs, it can auto-generate email campaigns and suggestions tailored to each lead. Nuform Social can use similar approaches to score leads, predict customer needs, and time follow-ups optimally. AI can also enrich customer profiles (e.g., summarizing customer interactions or extracting purchase intent), so the sales team focuses on the right accounts.
- Marketing Automation: Generative AI amplifies automation workflows. Chatbots on websites can qualify leads (engaging visitors with personalized questions and content). AI can write and schedule email newsletters or social posts based on analytics (e.g. posting the highest-converting copy at the best times). Tools like HubSpot and Mailchimp increasingly embed GPT features for automated drafting and testing. By automating these tasks, Nuform Social helps clients save on labor while scaling up campaigns.
- Interactive Content & Gamification: Agencies use AI to create engaging experiences. For instance, they might build an interactive quiz or chatbot-powered story on a brand’s site. Using image-generation AI (like DALL·E or Stable Diffusion), they can produce custom visuals or infographics quickly. Some agencies even add gamified elements – like social media filters or AI-driven games – to keep audiences engaged. The result is higher time-on-site and better lead generation. Importantly, AI makes these interactive campaigns affordable: what once required a design studio can now be prototyped in hours.
Cost-effectiveness and ROI: All these AI-driven tactics translate to big savings. As noted earlier, one AI marketing solution delivered 30× ROI to its clients. Another campaign cut customer acquisition costs by 97%. For an agency like Nuform Social, that means clients can see more leads per dollar spent. Internally, AI cuts content production time (e.g. faster campaign setup) so the agency’s team can serve more clients without headcount growth.
Compliance and Safety: Businesses also worry about compliance and accuracy. Here too, agencies apply best practices. They often use guardrails like fine-tuning models on client-approved data or running AI outputs through human review. For example, when Fluna automated legal drafting, it achieved 92% accuracy on sensitive documents by combining Vertex AI with secure pipelines. Similarly, Nuform Social ensures that AI-generated content adheres to brand and regulatory guidelines by configuring the models appropriately (for instance, using AI models hosted in a client’s private cloud). Salesforce’s Einstein GPT highlights this approach: it’s trained on a company’s own “trusted, real-time data” so that personal and proprietary information never leaks. The outcome is confidence in AI-driven marketing – the content is both creative and compliant with policies.
By embracing generative AI across SEO, content personalization, CRM, and automation, digital agencies like Nuform Social can deliver smarter digital strategies that are cheaper and faster. This dual emphasis on innovation and ROI is why business leaders are increasingly comfortable investing in AI tools: the numbers above show that even a modest AI pilot can pay for itself many times over.
Conclusion
GPT-4.5 and the coming GPT-5 are rapidly reshaping the future of work. These models supercharge productivity tools – from office software to code editors to CRM platforms – by automating creative and analytic tasks. Across industries, real-world use cases are popping up everywhere: marketing campaigns written by AI, HR bots answering employee questions, lawyers using AI for contract review, and customer support handled by chatbots. The early results are clear: organizations are reporting huge time savings, cost reductions, and ROI from generative AI. For example, companies using AI for marketing have seen 30× increases in campaign ROI, while others save thousands of work-hours monthly.
Of course, deploying this technology responsibly is crucial. Businesses must manage compliance, data privacy, and the risk of misinformation. That is why enterprise AI solutions emphasize safety and trusted data sources (for instance, GPT-4.5 is released as a “research preview” to study its strengths and limitations). Tech leaders advise a “lean forward” approach: experiment with pilots, measure outcomes, and scale what works. In doing so, companies can capture the immense benefits of AI.
For leaders and practitioners alike, the message is clear: the AI genie is out of the bottle. GPT-4.5 is already in our tools, and GPT-5 promises even broader capabilities. By integrating these models into everyday workflows – from content marketing to code writing to legal research – businesses can gain a competitive edge. The future of work will be one of human-AI collaboration, where AI handles routine creativity and data crunching, enabling people to focus on strategy, relationships, and innovation.